Data Review Process to Determine What Data Can Be in Cloud Computing
What is cloud computing?
Cloud calculating is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the internet. These services are divided into three main categories or types of deject computing: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform equally a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
A cloud can be private or public. A public cloud sells services to anyone on the internet. A private deject is a proprietary network or a data center that supplies hosted services to a limited number of people, with sure access and permissions settings. Private or public, the goal of cloud computing is to provide piece of cake, scalable access to calculating resources and It services.
Cloud infrastructure involves the hardware and software components required for proper implementation of a cloud computing model. Cloud computing can also be thought of as utility computing or on-need calculating.
The name cloud computing was inspired past the cloud symbol that's often used to represent the cyberspace in flowcharts and diagrams.
How does cloud computing work?
Cloud computing works by enabling client devices to access data and deject applications over the internet from remote concrete servers, databases and computers.
An internet network connection links the front end, which includes the accessing customer device, browser, network and cloud software applications, with the back finish, which consists of databases, servers and computers. The back terminate functions as a repository, storing information that is accessed by the front finish.
Communications between the front and back ends are managed by a fundamental server. The central server relies on protocols to facilitate the commutation of data. The cardinal server uses both software and middleware to manage connectivity between unlike client devices and cloud servers. Typically, there is a dedicated server for each individual application or workload.
Cloud computing relies heavily on virtualization and automation technologies. Virtualization enables the easy abstraction and provisioning of services and underlying deject systems into logical entities that users can request and use. Automation and accompanying orchestration capabilities provide users with a high degree of cocky-service to provision resources, connect services and deploy workloads without direct intervention from the deject provider'due south It staff.
Types of cloud calculating services
Cloud calculating can be separated into three full general service delivery categories or forms of deject calculating:
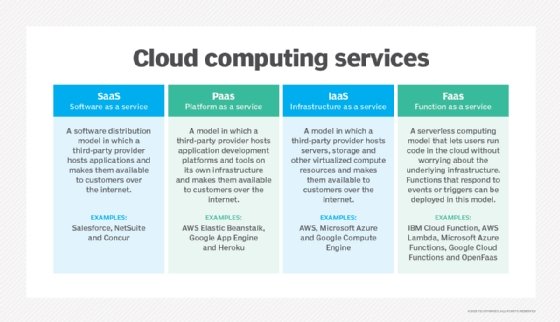
- IaaS . IaaS providers, such equally Amazon Web Services (AWS), supply a virtual server case and storage, as well as application programming interfaces (APIs) that let users migrate workloads to a virtual machine (VM). Users take an allocated storage capacity and can kickoff, stop, access and configure the VM and storage as desired. IaaS providers offering pocket-sized, medium, large, extra-large, and retention- or compute-optimized instances, in improver to enabling customization of instances, for various workload needs. The IaaS cloud model is closest to a remote data center for business users.
- PaaS . In the PaaS model, cloud providers host development tools on their infrastructures. Users access these tools over the net using APIs, web portals or gateway software. PaaS is used for general software development, and many PaaS providers host the software after it's adult. Common PaaS products include Salesforce's Lightning Platform, AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Google App Engine.
- SaaS . SaaS is a distribution model that delivers software applications over the cyberspace; these applications are often called web services. Users tin access SaaS applications and services from any location using a calculator or mobile device that has net access. In the SaaS model, users gain access to application software and databases. One common case of a SaaS application is Microsoft 365 for productivity and email services.
Deject computing deployment models
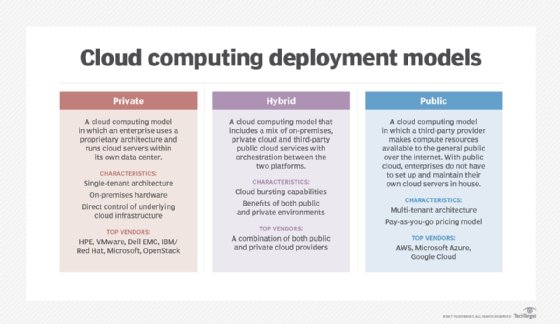
Private cloud services are delivered from a business'southward information center to internal users. With a private deject, an organization builds and maintains its own underlying cloud infrastructure. This model offers the versatility and convenience of the cloud, while preserving the management, command and security common to local data centers. Internal users might or might not be billed for services through Information technology chargeback. Mutual individual deject technologies and vendors include VMware and OpenStack.
In the public cloud model, a third-political party cloud service provider (CSP) delivers the cloud service over the cyberspace. Public cloud services are sold on demand, typically by the minute or hour, though long-term commitments are bachelor for many services. Customers only pay for the key processing unit cycles, storage or bandwidth they consume. Leading public CSPs include AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM and Google Deject Platform (GCP), as well equally IBM, Oracle and Tencent.
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public cloud services and an on-bounds private cloud, with orchestration and automation between the two. Companies can run mission-critical workloads or sensitive applications on the private cloud and utilize the public cloud to handle workload bursts or spikes in demand. The goal of a hybrid cloud is to create a unified, automated, scalable environs that takes advantage of all that a public cloud infrastructure can provide, while notwithstanding maintaining control over mission-disquisitional data.
In improver, organizations are increasingly embracing a multi-cloud model, or the use of multiple IaaS providers. This enables applications to migrate betwixt different cloud providers or to even operate concurrently across 2 or more cloud providers.
Organizations adopt multi-cloud for various reasons. For example, they could do so to minimize the risk of a cloud service outage or to take advantage of more competitive pricing from a particular provider. Multi-deject implementation and application development can be a challenge because of the differences between deject providers' services and APIs.
Multi-cloud deployments should get easier, nonetheless, as providers' services and APIs converge and get more than standardized through industry initiatives such every bit the Open Cloud Calculating Interface.
A community deject, which is shared by several organizations, supports a particular community that shares the same concerns -- e.g., the aforementioned mission, policy, security requirements and compliance considerations. A customs deject is either managed past these organizations or a third-party vendor and can be on or off bounds.
Characteristics and advantages of deject calculating
Cloud calculating has been around for several decades at present, and today'southward cloud calculating infrastructure demonstrates an array of characteristics that have brought meaningful benefits for businesses of all sizes. Some of the main characteristics of cloud computing are the following:
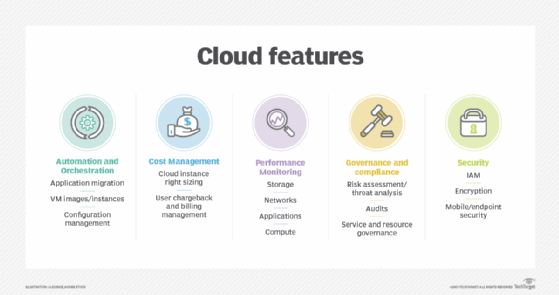
- Cocky-service provisioning . Terminate users can spin upwards compute resources for almost whatever blazon of workload on demand. An stop user can provision computing capabilities, such as server fourth dimension and network storage, eliminating the traditional need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
- Elasticity . Companies tin freely calibration up as computing needs increase and scale down once again as demands decrease. This eliminates the demand for massive investments in local infrastructure, which might or might not remain agile.
- Pay per use . Compute resources are measured at a granular level, enabling users to pay but for the resources and workloads they use.
- Workload resilience. CSPs often implement redundant resource to ensure resilient storage and to keep users' important workloads running -- oft across multiple global regions.
- Migration flexibility. Organizations can motility certain workloads to or from the cloud -- or to different cloud platforms -- equally desired or automatically for amend cost savings or to use new services every bit they sally.
- Broad network admission. A user can access cloud data or upload data to the deject from anywhere with an net connection using whatsoever device.
- Multi-tenancy and resource pooling. Multi-tenancy lets numerous customers share the same physical infrastructures or the same applications withal still retain privacy and security over their own information. With resources pooling, cloud providers service numerous customers from the aforementioned physical resources. The resource pools of the cloud providers should be big and flexible plenty then they can service the requirements of multiple customers.
These characteristics support a variety of important benefits for modern business concern, including the following:
- Cost direction. Using cloud infrastructure tin can reduce capital costs, as organizations don't have to spend massive amounts of money buying and maintaining equipment. This reduces their capital expenditure costs -- as they don't accept to invest in hardware, facilities, utilities or building large data centers to accommodate their growing businesses. Additionally, companies don't need large It teams to handle cloud data center operations because they can rely on the expertise of their deject providers' teams. Cloud computing besides cuts costs related to reanimation. Since downtime rarely happens in deject computing, companies don't accept to spend time and coin to fix any issues that might exist related to downtime.
- Information and workload mobility. Storing data in the cloud means that users tin can access it from anywhere with any device with simply an internet connectedness. That means users don't take to carry around USB drives, an external hard drive or multiple CDs to access their data. Users can access corporate data via smartphones and other mobile devices, enabling remote employees to stay upwardly to date with co-workers and customers. End users can easily process, shop, remember and recover resource in the cloud. In addition, cloud vendors provide all the upgrades and updates automatically, saving fourth dimension and effort.
- Business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR). All organizations worry well-nigh data loss. Storing data in the deject guarantees that users can always admission their data even if their devices, east.g., laptops or smartphones, are inoperable. With cloud-based services, organizations can quickly recover their information in the outcome of emergencies, such as natural disasters or ability outages. This benefits BCDR and helps ensure that workloads and data are available fifty-fifty if the business organisation suffers damage or disruption.
Disadvantages of cloud computing
Despite the articulate upsides to relying on deject services, cloud calculating carries its own challenges for It professionals:
- Cloud security . Security is often considered the greatest claiming facing cloud calculating. When relying on the cloud, organizations hazard information breaches, hacking of APIs and interfaces, compromised credentials and authentication issues. Furthermore, at that place is a lack of transparency regarding how and where sensitive data entrusted to the cloud provider is handled. Security demands careful attention to cloud configurations and business policy and practice.
- Cost unpredictability . Pay-every bit-you lot-go subscription plans for cloud use, along with scaling resources to conform fluctuating workload demands, can make information technology tough to define and predict final costs. Cloud costs are as well frequently interdependent, with one cloud service often utilizing one or more than other cloud services -- all of which appear in the recurring monthly pecker. This can create additional unplanned cloud costs.
- Lack of capability and expertise . With cloud-supporting technologies chop-chop advancing, organizations are struggling to keep upward with the growing demand for tools and employees with the proper skill sets and knowledge needed to builder, deploy, and manage workloads and data in a cloud.
- IT governance. The emphasis on practise-it-yourself capability in cloud computing can get in governance hard, as there is no control over provisioning, deprovisioning and management of infrastructure operations. This can make it challenging to properly manage risks and security, Information technology compliance and data quality.
- Compliance with manufacture laws . When transferring data from on-bounds local storage into cloud storage, it tin can be difficult to manage compliance with industry regulations through a third political party. Information technology's of import to know where data and workloads are actually hosted in order to maintain regulatory compliance and proper business governance.
- Management of multiple clouds . Every cloud is different, and then multi-cloud deployments can disjoint efforts to address more general cloud calculating challenges.
- Cloud performance . Performance -- such as latency -- is largely beyond the control of the organization contracting cloud services with a provider. Network and provider outages can interfere with productivity and disrupt business organisation processes if organizations are not prepared with contingency plans.
- Building a private cloud . Architecting, building and managing private clouds -- whether for its own purpose or for a hybrid cloud goal -- can be a daunting task for IT departments and staff.
- Cloud migration . The process of moving applications and other data to a cloud infrastructure often causes complications. Migration projects frequently take longer than predictable and go over budget. The issue of workload and data repatriation -- moving from the deject dorsum to a local data center -- is ofttimes overlooked until unforeseen toll or performance problems arise.
- Vendor lock-in. Oft, switching betwixt deject providers can cause pregnant issues. This includes technical incompatibilities, legal and regulatory limitations and substantial costs incurred from sizable data migrations.
Cloud calculating examples and utilize cases
Cloud calculating has evolved and diversified into a broad assortment of offerings and capabilities designed to conform near any conceivable business need. Examples of cloud computing capabilities and diversity include the post-obit:
- Google Docs, Microsoft 365. Users can access Google Docs and Microsoft 365 through the internet. Users tin exist more productive because they tin access work presentations and spreadsheets stored in the cloud at anytime from anywhere on whatever device.
- Email, Calendar, Skype, WhatsApp. Emails, calendars, Skype and WhatsApp take reward of the deject's ability to provide users with access to data remotely so they can access their personal data on any device, whenever and wherever they want.
- Zoom. Zoom is a cloud-based software platform for video and sound conferencing that records meetings and saves them to the cloud, enabling users to access them anywhere and at any time. Another common communication and collaboration platform is Microsoft Teams.
- AWS Lambda. Lambda enables developers to run code for applications or back-end services without having to provision or manage servers. The pay-as-you-go model constantly scales with an organization to adjust real-fourth dimension changes in data usage and data storage. Other major cloud providers also support serverless computing capabilities, such as Google Cloud Functions and Azure Functions.
And then, how is the deject actually used? The myriad services and capabilities found in modern public clouds have been practical across countless use cases, such as the following:
- Testing and evolution. Ready-made, tailored environments can expedite timelines and milestones.
- Production workload hosting. Organizations are using the public deject to host live production workloads. This requires careful design and architecture of cloud resources and services needed to create an adequate operational environment for the workload and its required level of resilience.
- Big information analytics . Remote data centers through deject storage are flexible and scalable and tin can provide valuable data-driven insights. Major cloud providers offer services tailored to big data projects, such every bit Amazon EMR and Google Cloud Dataproc.
- IaaS. IaaS enables companies to host Information technology infrastructures and access compute, storage and network capabilities in a scalable manner. Pay-every bit-you-become subscription models tin can help companies relieve on upfront IT costs.
- PaaS. PaaS can assistance companies develop, run and manage applications in an easier and more flexible way, at a lower cost than maintaining a platform on bounds. PaaS services can also increase development speed for applications and enables higher-level programming.
- Hybrid cloud. Organizations take the option to use the appropriate cloud -- private or public -- for dissimilar workloads and applications to optimize cost and efficiency according to the circumstance.
- Multi-deject. Using multiple unlike deject services from split up deject providers can assist subscribers find the all-time cloud service fit for diverse workloads with specific requirements.
- Storage. Big amounts of information can be stored remotely and accessed easily. Clients only have to pay for storage that they actually use.
- DR. Deject offers faster recovery than traditional on-bounds DR. Furthermore, it is offered at lower costs.
- Data backup. Deject backup solutions are more often than not easier to utilise. Users do not have to worry nearly availability and capacity, and the cloud provider manages data security.
Cloud calculating vs. traditional web hosting
Given the many different services and capabilities of the public cloud, at that place has been some defoliation between cloud computing and major uses, such every bit web hosting. While the public cloud is often used for spider web hosting, the two are quite different. A cloud service has three distinct characteristics that differentiate it from traditional spider web hosting:
- Users can admission large amounts of computing power on demand. Information technology is typically sold by the minute or the hour.
- Information technology is elastic -- users tin can accept equally much or as little of a service as they want at whatsoever given time.
- The service is fully managed by the provider -- the consumer needs nada only a personal estimator and cyberspace access. Significant innovations in virtualization and distributed calculating, likewise every bit improved access to high-speed internet, accept accelerated interest in cloud computing.
Deject calculating service providers
The cloud service market has no shortage of providers. The iii largest public CSPs that have established themselves as dominant fixtures in the industry are the following:
- AWS
- GCP
- Microsoft Azure
Other major CSPs include the following:
- Apple
- Citrix
- IBM
- Salesforce
- Alibaba
- Oracle
- VMware
- SAP
- Joyent
- Rackspace
When considering a cloud service vendor, certain considerations should be taken. First, the actual suite of services tin can vary between providers, and business organization users must select a provider that offers services -- such as big data analytics or artificial intelligence (AI) services -- that support the intended apply case.
Though cloud services typically rely on a pay-per-use model, different providers often accept variations in their pricing plans to consider. Furthermore, if the cloud provider will be storing sensitive data, concrete location of the provider's servers should also be considered.
Naturally, reliability and security should be top priorities. A provider's service-level agreement should specify a level of service uptime that is satisfactory to client business organisation needs. When considering different cloud vendors, shut attention should be given to what technologies and configuration settings are used to secure sensitive information.
Cloud computing security
Security remains a primary business for businesses contemplating cloud adoption -- especially public cloud adoption. Public CSPs share their underlying hardware infrastructure between numerous customers, as the public deject is a multi-tenant environment. This environment demands significant isolation betwixt logical compute resources. At the same fourth dimension, admission to public cloud storage and compute resources is guarded by account login credentials.
Many organizations spring by complex regulatory obligations and governance standards are still hesitant to place data or workloads in the public cloud for fearfulness of outages, loss or theft. All the same, this resistance is fading, as logical isolation has proven reliable and the addition of information encryption and diverse identity and access management tools have improved security within the public cloud.
Ultimately, the responsibility for establishing and maintaining a secure cloud environs falls to the private concern user that is responsible for building the workload's architecture -- the combination of deject resources and services in which the workload runs -- and implementing the security features that the deject provider offers.
History of cloud computing
The history and evolution of cloud computing date back to the 1950s and 1960s.
In the 1950s, companies started to use big mainframe computers, just it was too expensive to buy a reckoner for each user. And so, during the late 1950s and early 1960s, a process called fourth dimension sharing was developed to make more efficient use of expensive processor time on the central mainframe.
Time sharing enabled users to access numerous instances of computing mainframes simultaneously, maximizing processing ability and minimizing reanimation. This thought represents the first utilise of shared computing resources, the foundation of modern cloud computing.
The origins of delivering calculating resources using a global network are, for the most office, rooted in 1969 when American estimator scientist J.C.R. Licklider helped create the Avant-garde Enquiry Projects Agency Network, the and then-called precursor to the internet. Licklider's goal was to connect computers across the earth in a way that would enable users to access programs and information from whatsoever location.
In the 1970s, cloud computing began taking a more tangible shape with the introduction of the first VMs, enabling users to run more than than one computing system inside a single concrete setup. The functionality of these VMs led to the concept of virtualization, which had a major influence on the progress of cloud calculating.
In the 1970s and 1980s, Microsoft, Apple and IBM adult technologies that enhanced the cloud environment and advanced the use of the deject server and server hosting. Then, in 1999, Salesforce became the first company to deliver business applications from a website.
In 2006, Amazon launched AWS, providing such services equally calculating and storage in the cloud. Following suit, the other major tech players, including Microsoft and Google, afterward launched their own deject offerings to compete with AWS.
Future of deject calculating and emerging technologies
Over thirty% of enterprise It conclusion-makers identified public cloud equally their meridian priority in 2019, co-ordinate to the "RightScale 2019 Land of the Deject Study." Still, enterprise adoption of the public cloud, especially for mission-critical applications, hasn't been happening as quickly equally many experts predicted.
Today, however, organizations are more likely to migrate mission-critical workloads to public clouds. 1 of the reasons for this shift is that business concern executives who desire to ensure that their companies tin can compete in the new globe of digital transformation are enervating the public cloud.
Business concern leaders are also looking to the public cloud to have advantage of its elasticity, modernize internal reckoner systems, and empower critical business units and their DevOps teams.
Additionally, cloud providers, such as IBM and VMware, are concentrating on coming together the needs of enterprise It, in part by removing the barriers to public cloud adoption that caused Information technology decision-makers to shy away from fully embracing the public deject previously.
More often than not, when contemplating cloud adoption, many enterprises have been mainly focused on new cloud-native applications -- that is, designing and building applications specifically intended to use cloud services. They haven't been willing to move their well-nigh mission-critical apps into the public deject. However, these enterprises are at present beginning to realize that the cloud is ready for the enterprise if they select the right cloud platforms, i.due east., those that have a history of serving the needs of the enterprise.
Cloud providers are locked in ongoing competition for cloud market place share, so the public cloud continues to evolve, expand and diversify its range of services. This has led public IaaS providers to offering far more than common compute and storage instances.
For example, serverless, or event-driven, computing is a cloud service that executes specific functions, such as image processing and database updates. Traditional cloud deployments require users to establish a compute instance and load code into that instance. Then, the user decides how long to run -- and pay for -- that instance.
With serverless computing, developers simply create lawmaking, and the deject provider loads and executes that code in response to real-world events so users don't have to worry about the server or example aspect of the cloud deployment. Users only pay for the number of transactions that the function executes. AWS Lambda, Google Deject Functions and Azure Functions are examples of serverless computing services.
Public cloud computing also lends itself well to big data processing, which demands enormous compute resources for relatively short durations. Cloud providers accept responded with big information services, including Google BigQuery for large-scale data warehousing and Microsoft Azure Data Lake Analytics for processing huge data sets.
Another crop of emerging cloud technologies and services relates to AI and machine learning. These technologies provide a range of cloud-based, set-to-use AI and auto learning services for client needs. Amazon Machine Learning, Amazon Lex, Amazon Polly, Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine and Google Cloud Speech API are examples of these services.
parrishsullumeent.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcloudcomputing/definition/cloud-computing
0 Response to "Data Review Process to Determine What Data Can Be in Cloud Computing"
Post a Comment